A Complete Guide To Gate Valve
What is a Gate Valve?
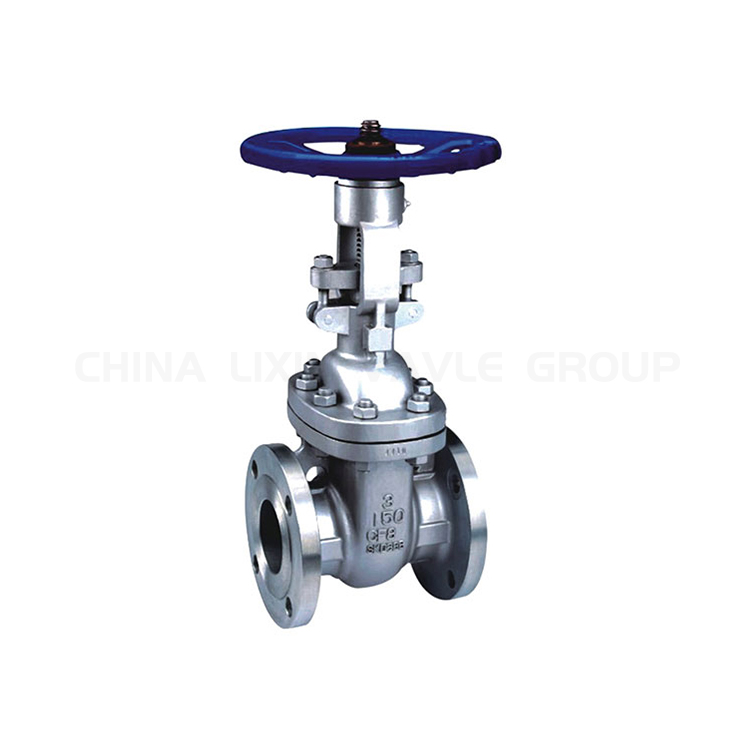

Gate valves are a common type of valve used to control the flow of fluids. It has a simple structure and consists of a gate valve body, gate valve bonnet, gate valve stem and valve flap. The valve flap is usually a flat or circular door plate that can be controlled to open or close by rotating the stem. When the valve flap is open, the fluid can pass through the valve smoothly; when closed, the valve can completely stop the flow of fluid. Gate valves are used in applications where the flow of fluid needs to be completely shut off at once, such as during pipeline maintenance or emergency situations. Due to their simple and reliable design, gate valves are widely used in a variety of industrial applications, such as petrochemical, water treatment and heating systems.
Gate Valve Symbol
Gate valve symbols usually consist of a set of simple geometric shapes. In a flowchart, gate valve is usually represented as a rectangle with a diagonal line above it to indicate the position of the valve. Sometimes there is also a dot within the rectangle indicating the position of the valve. These symbols are intended to clearly express the location and status of the valve so that engineers and operators can accurately understand the flowchart and equipment layout. The standardization of gate valve symbols helps to ensure that uniform symbols are used in engineering drawings and flow charts, which improves communication and understanding, and reduces the potential for misunderstandings and errors.
Gate Valve Parts

Gate valves include key components such as valve body, bonnet, stem, seat, gate and seals. The body is the main housing of the gate valve, carrying the internal components and providing the connection to the piping. The gate valve bonnet is used to cover the top of the valve body to protect the internal mechanism and ensure sealing performance. The valve stem is the key component used to control the movement of the gate, through the rotation or up and down to control the opening and closing of the valve. The seat is located inside the valve body and works in conjunction with the gate to ensure a complete seal when the valve is closed. The gate is the key component to control the flow of the medium, by moving up and down to regulate the passage of the medium. Finally, the seal is to ensure that the valve sealing performance is an important part of the components, including packing, sealing ring and so on. These components cooperate with each other and together constitute the core structure of the gate valve, ensuring its reliable operation and long-term use in the pipeline system.
Gate Valve Types
There are several types of gate valves, each designed to suit specific applications and operational requirements:
- Parallel Gate Valve: This type of valve features two parallel seats where the gate moves up and down between them. When fully open, the gate retracts into the valve body, allowing unobstructed flow. Parallel gate valves are preferred for applications requiring minimal pressure drop.
- Wedge Gate Valve: Unlike the parallel gate valve, the wedge gate valve has a single gate that moves perpendicular to the flow direction. The gate features a wedge-shaped design, which provides a tight seal against the valve seats, even in high-pressure environments. Wedge gate valves are commonly used in systems where a tight shut-off is necessary.
- Slab Gate Valve: Slab gate valves are designed for applications requiring bi-directional flow control. They feature a flat gate that slides across the flow path to open or close the valve. These valves offer excellent sealing capabilities and are often used in the oil and gas industry for pipeline isolation.
- Knife Gate Valve: Knife gate valves are specially designed for handling slurries, powders, and other viscous media. They feature a sharp-edged gate that cuts through the flow, minimizing clogging and ensuring a tight shut-off. Knife gate valves are widely used in wastewater treatment plants, pulp and paper mills, and mining operations.
- Conduit Gate Valve: Conduit gate valves, also known as expanding gate valves, utilize a mechanism where the gate expands against the valve seats when closing, providing a tight seal even in high-pressure applications. These valves are commonly used in pipelines for natural gas transmission and other critical fluid control systems.
Gate Valve Function
The primary function of gate valves is to provide fast, reliable closure to prevent the flow of fluid when needed. They are typically used in applications that require frequent opening and closing, as they are designed to withstand frequent operation without damage. In addition, gate valves provide a lower pressure drop, which means that fluid can flow more easily through the piping, reducing the energy consumption and operating costs of the system.
How Does a Gate Valve Work?

Gate valves work on a simple principle, controlling the flow of fluid primarily by moving the valve spool (also known as the valve gate or valve flap). Specifically, when the gate valve is closed, the valve spool is located in the fluid passage of the pipeline, parallel to the inner wall of the pipeline, blocking the passage of fluid. When the valve needs to be opened, the spool is moved upward or downward away from or near the fluid passage of the pipe by rotating the handle or operating device. When the valve spool is fully open, the fluid can pass freely through the pipe; when the valve spool is fully closed, the spool is in close contact with the inner wall of the pipe, blocking the passage of the fluid.
How to Use a Gate Valve?
To ensure safe and efficient operation of your system, follow these steps when operating the gate valve:
Check the position: Before operating, make sure the gate valve is closed. The closed position is indicated by the handle being perpendicular to the piping direction.
Open the valve: turn the handle counterclockwise until the handle is parallel to the pipeline axis, then the valve is fully open.
Close the valve: turn the handle clockwise until the handle is perpendicular to the pipeline axis, then the valve is completely closed.
Periodic Inspection: It is recommended that you inspect the gate valve periodically for leaks or damage to ensure proper operation.
Avoid excessive force: When operating the gate valve, avoid excessive force to prevent damage to the valve or piping.
Maintenance: Refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance, such as regular lubrication of the gate valve, to ensure smooth operation.
Remember: Use caution when operating the gate valve to ensure safe and efficient operation of the system.
How to Fix a Gate Valve That Doesn’t Close
When a gate valve fails to close, the following steps may need to be performed to fix it:
Clean The Valve: First check around the valve for debris or dirt that may be preventing the valve from closing. Remove the buildup with a cleaner and brush.
Lubricate The Valve: Moving parts of the valve may be difficult to close due to lack of lubrication. Add lubricant in the proper places to ensure smooth valve movement.
Adjust Valve: Check the valve’s operating mechanism to ensure there are no damaged or loose parts. If necessary, adjust the valve components to ensure that it will close properly.
Replace Seals: If the valve still won’t close, a damaged seal may be the cause. Inspect and replace any worn or broken seals to restore the valve’s sealing performance.
Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance can prevent similar problems. Cleaning and lubricating the valve and periodically checking its operation will extend its life and ensure that it works properly.
If none of these methods solve the problem, you may want to consider replacing the valve or seeking professional assistance.
Gate Valve vs Butterfly Valve
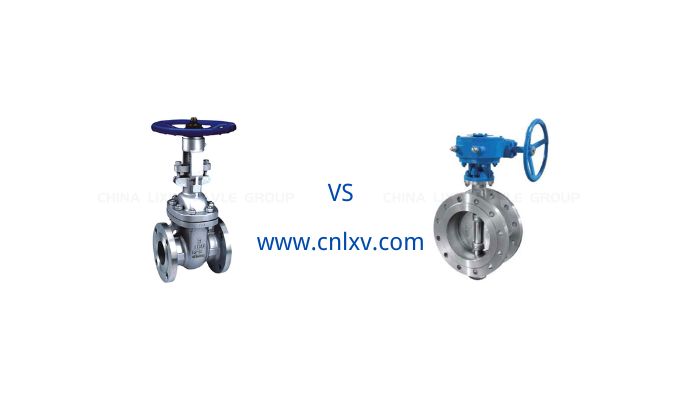

When you need to choose the right valve for your fluid control system, you’re often faced with the choice between a Gate valve and a butterfly valve. Although they are both common types of valves used in fluid control, they each have their own characteristics in terms of design, application, and performance.
Gate valves are typically used in applications where fluid needs to be tightly shut off or opened. They are simple in design and typically have a gated gate to control the flow of fluid. This makes them effective where low resistance and high flow rates are required, but they can cause noise and vibration when partially open.
In contrast, butterfly valves have a simpler design with a rotating disk that controls the fluid. They can be opened and closed more quickly and cause relatively low pressure loss in the fully open or fully closed position. Butterfly valves are typically used in applications that require frequent operation and lower pressure drops.
Therefore, choosing the right type of valve is critical when you need to consider factors such as fluid control accuracy, frequency of operation, and system pressure loss. gate valves and butterfly valves each have their own advantages, and choosing one based on the specific needs of your application can maximize system efficiency and ensure consistent fluid control.
Gate Valve vs Globe Valve
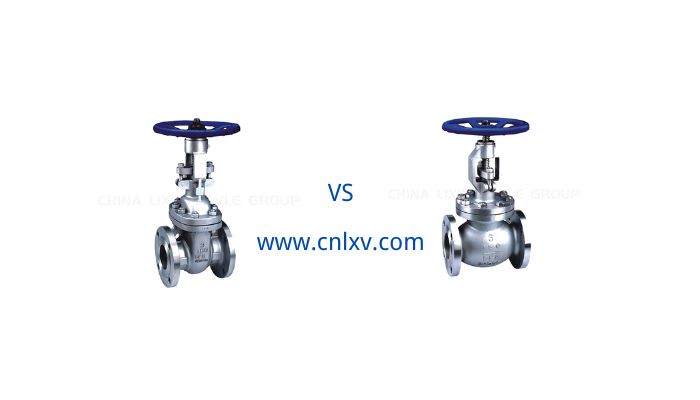

Gate valves are typically used in applications where fluid flow needs to be fully opened or closed. Their design allows them to provide a small pressure drop and less resistance when fully open. Gate valves are typically used in applications that require frequent operation because they are designed to minimize wear and damage. However, gate valves are not suitable for applications that require flow regulation or control of fluid flow in a partially open state.
Globe valves are better suited for applications that require flow regulation or control of fluid flow in a partially open position. Globe valves have a more complex design and typically include an adjustable spool that can be rotated to regulate the flow of fluid. Globe valves are more flexible in regulating flow, but they may incur a greater pressure drop compared to gate valves.
Therefore, when choosing between gate and globe valves, you need to consider your specific needs and application scenarios. If you need to simply open or close the fluid flow and need a smaller pressure drop, then a gate valve may be a better choice. However, if you need to regulate flow or control fluid flow in a partially open state, then a globe valve may be more suitable for your needs.
Top Gate Valve Manufacturers
When talking about the top gate valve manufacturers, Lixin Valve Group has to be mentioned. As one of the leaders in the industry, Lixin Valve Group is known for its superior product quality, innovative engineering solutions and excellent customer service. Whether in the fields of municipal engineering, petrochemical, power, metallurgy, construction, etc., Lixin Valve Group provides customers with a wide range of gate valve products and solutions.
Lixin Valve Group’s gate valve products are carefully designed and rigorously tested to ensure their reliability and durability in a variety of application environments. In addition to this, Lixin Valve Group is constantly investing in research and development, and is committed to driving technological innovation to meet the needs of an ever-evolving market. Whether it is a standard product or a customized solution, Lixin Valve Group has won the trust and praise of customers with its quality products and services.
Globally, Lixin Valve Group has established a strong sales network and a perfect after-sales service system to provide customers with timely and professional support and service. As one of the top gate valve manufacturers, Lixin Valve Group is always committed to creating greater value for customers and becoming their trusted partner!
FAQs on Gate Valve
Q1: How to choose the right gate valve?
When selecting a gate valve, you need to consider factors such as fluid medium, pressure, temperature, flow requirements and pipe size. In addition, the valve’s material, sealing performance and operation mode need to be considered.
Q2: How to solve the gate valve leakage problem?
Typically, gate valve leakage problems can be solved by inspecting and replacing seals, adjusting the gate position, or repairing the valve operating mechanism. If necessary, valve replacement may also be considered.
Q3: Can gate valves be used in high temperature/high pressure applications?
Yes, gate valves can be designed for use in high temperature and high pressure environments. When selecting a gate valve, it is important to ensure that the material and design meet the temperature and pressure requirements of the application.
Q4: Why do gate valves require some redundancy in operation?
Allowing for redundant space ensures that the valve will not be overstressed by piping expansion or other factors during normal operation, thus increasing the life and reliability of the valve.
Q5: How do I determine if a gate valve is suitable for a particular fluid medium?
The choice of material for a gate valve usually depends on the chemical nature and corrosiveness of the fluid medium. Common materials include cast iron, carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel. When selecting a gate valve, the characteristics of the fluid medium and the corrosion resistance of the valve material must be considered.
Want To Explore More Quality Products?











