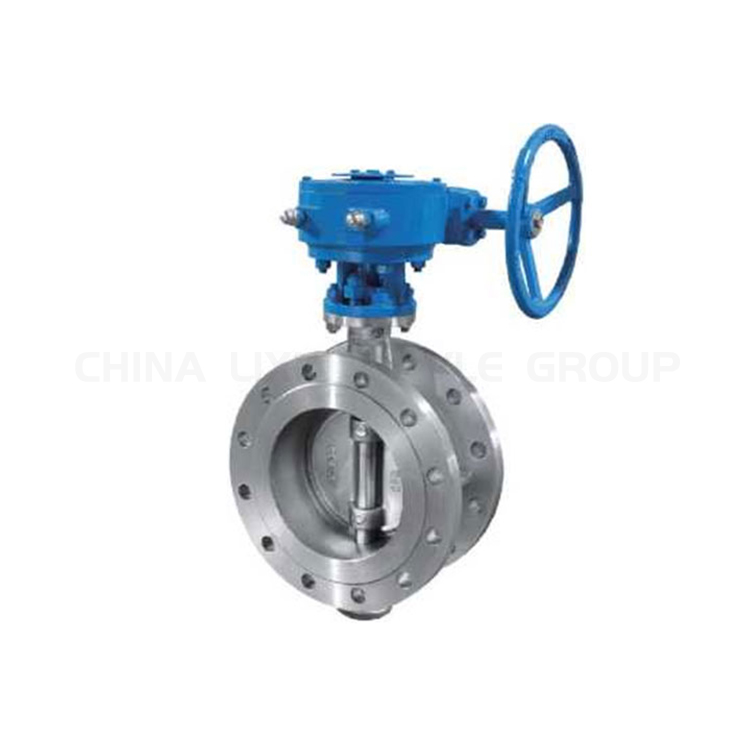
What is a Plug Valve?
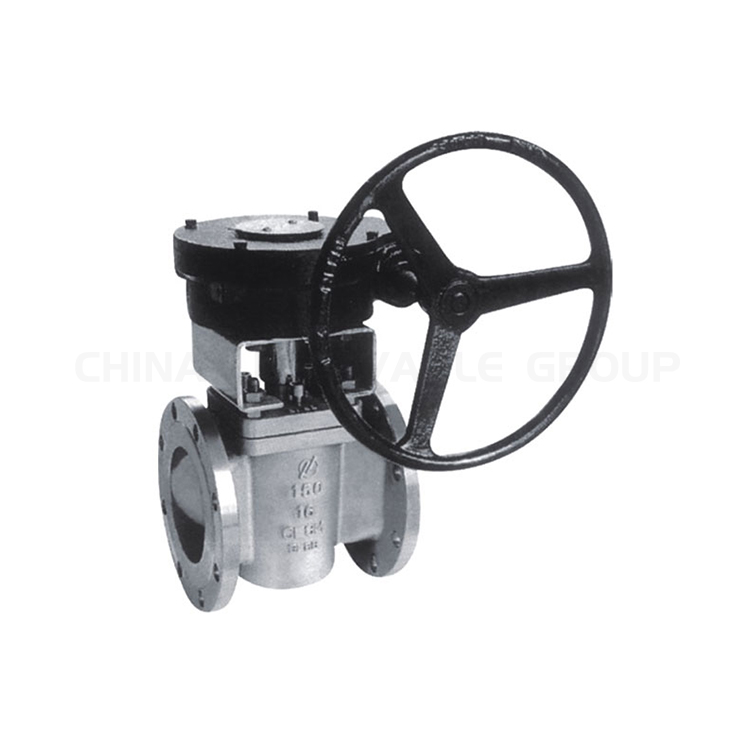

A plug valve is a valve that utilizes rotation for on/off control. Its core component is a cylindrical or conical plug with an internal passageway. By rotating the plug 90 degrees, the passageway can be aligned with or perpendicular to the flow path to open or close the fluid. Plug valves are widely used in a variety of fluid control applications due to their simple and efficient design.
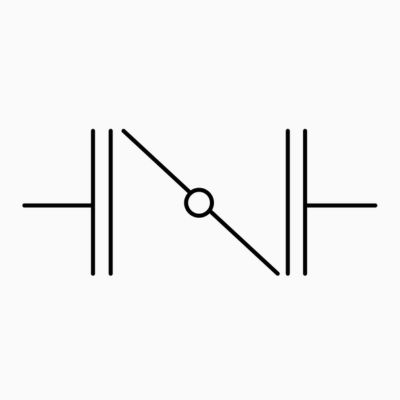
Plug Valve Symbol
At the heart of the plug valve symbol is a rectangle with diagonal lines, subtly symbolizing the plug itself and its unique rotary action. This basic symbol is not set in stone, however, and can be adapted to suit specific conditions. The direction of flow is clearly indicated by the addition of an arrow that shows the direction in which the medium flows through the plug. In addition to special functions, additional lines can indicate specific attributes such as lubrication functions, multi-port configurations, etc., making the symbol even more informative.
Types of Plug Valves
Several types of plug valves cater to specific needs and applications:
Lubricated Plug Valve
Utilizes a lubricant to reduce friction between the plug and valve body for smooth operation and to prevent wear. Suitable for high pressure and high temperature applications.
Eccentric Plug Valve
Features an offset plug that produces a cam action when rotated. Provides a tight seal to minimize wear. For applications handling abrasive or fibrous media.
3 Way Plug Valve
Versatile valve with three ports for diverting or mixing flow. Widely used in piping and process systems where control of flow direction is required.
How Does a Plug Valve Work?

Operating a plug valve is a breeze. Turning the lever or actuator rotates the valve plug inside the valve body. When the opening of the plug aligns with the inlet and outlet, the valve opens and fluid flows. Rotating the plug 90 degrees blocks the flow path, effectively closing the valve. The tight seal created by the valve plug minimizes leakage.
What is a Plug Valve Used For?
Known for their versatility and reliability, plug valves are widely used in the following industries:
Oil and gas: control the flow of oil, gas and other hydrocarbons in pipelines, refineries and offshore platforms.
Chemical Processing: Resistant to corrosion and can handle a wide range of chemicals, making them ideal for chemical processing plants.
Water Treatment: Controls the flow and distribution of water in water treatment facilities.
Power Generation: Controls steam, water and other fluids in power plants.
Pharmaceutical: Hygienic design for pharmaceutical applications to ensure cleanliness in the manufacturing process.
Click To Watch Plug Valve Video>>
What is the Purpose of a Plug Valve?
Plug valves play a vital role in controlling the flow of liquids or gases. They are known for their reliable closing ability, excellent resistance to high pressures and extreme temperatures, and resistance to corrosion. These features make them the ideal solution for applications such as: tightly sealed shutoff to prevent flow leakage. High pressure environments, withstanding extreme pressure conditions. High temperature applications, maintaining their performance and reliability. Corrosive environments, resisting chemical attack and deterioration. Wholesale Plug Valve Supplier
Plug Valve vs Ball Valve
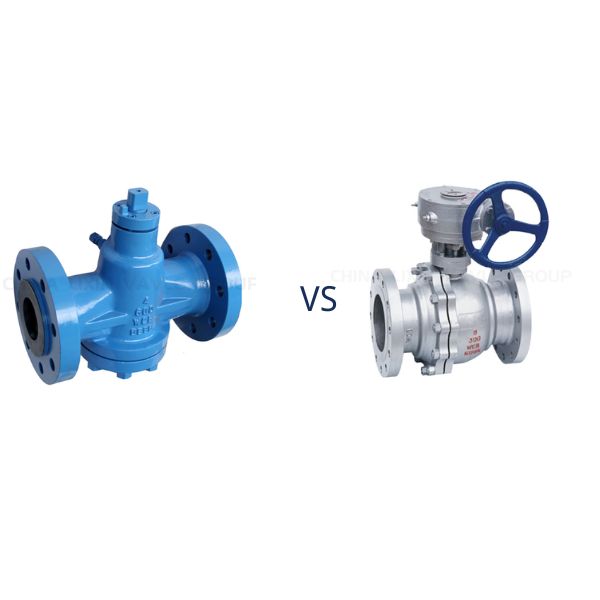

Plug and ball valves are both quarter-turn rotary valves, but differ in design and function:
Plug valves use a cylindrical or conical plug as the sealing element, while ball valves use a perforated sphere.
Plug valves have linear flow characteristics, i.e. the valve opening is proportional to the flow rate. Ball valves, on the other hand, exhibit more equi-percentage flow characteristics, which means that the relationship between valve opening and flow rate is more non-linear.
Plug valves typically provide a tighter seal due to their tight tolerances and lubrication capabilities. Ball valves provide a reliable seal due to the large surface contact area between the ball and seat.
Plug valves are used in applications where tight sealing and handling of viscous fluids are required, such as in the oil and gas industry. Ball valves are more suitable for applications with high pressure, high speed and low maintenance requirements, such as the water treatment and pharmaceutical sectors.
Top Plug Valve Manufacturers
Several reputable plug valve manufacturers produce high–quality plug valves, including:
-
Emerson
-
Flowserve
-
ITT Engineered Valves
-
Schlumberger
-
Cameron
FAQs on Plug Valves
What are the types of plug valves?
According to the structure and function, plug valves can be divided into many types, the common ones are: straight-through, three-way, four-way, lubricated, non-lubricated, soft sealing, hard sealing and so on.
What are the advantages of plug valves?
Plug valves have the following advantages: simple structure, rapid switching, low fluid resistance, good sealing performance, easy maintenance, long service life and so on.
How to choose the right plug valve?
When choosing plug valves, you need to consider the following factors: media type, pressure level, temperature range, connection, material, operation mode, etc.
How to maintain the plug valve?
Maintenance of plug valves includes: regular inspection of valve sealing performance, lubrication of the valve, cleaning the valve body and spool, and replacement of worn parts.
What are the differences between plug valves and ball valves?
Plug valves and ball valves are both common quarter-turn valves, but they differ in structure and performance. The fluid passage of a plug valve is a cylindrical or conical orifice, while the fluid passage of a ball valve is a spherical orifice. Generally speaking, plug valves offer less fluid resistance than ball valves, but the regulating performance is not as good as that of ball valves.
How can I tell if a plug valve needs repair or replacement?
Plug valves may need repair or replacement when the following conditions occur: leakage, difficulty in opening and closing, excessive operating torque, unusual noise or vibration of the valve, etc.




 Request a Quote
Request a Quote